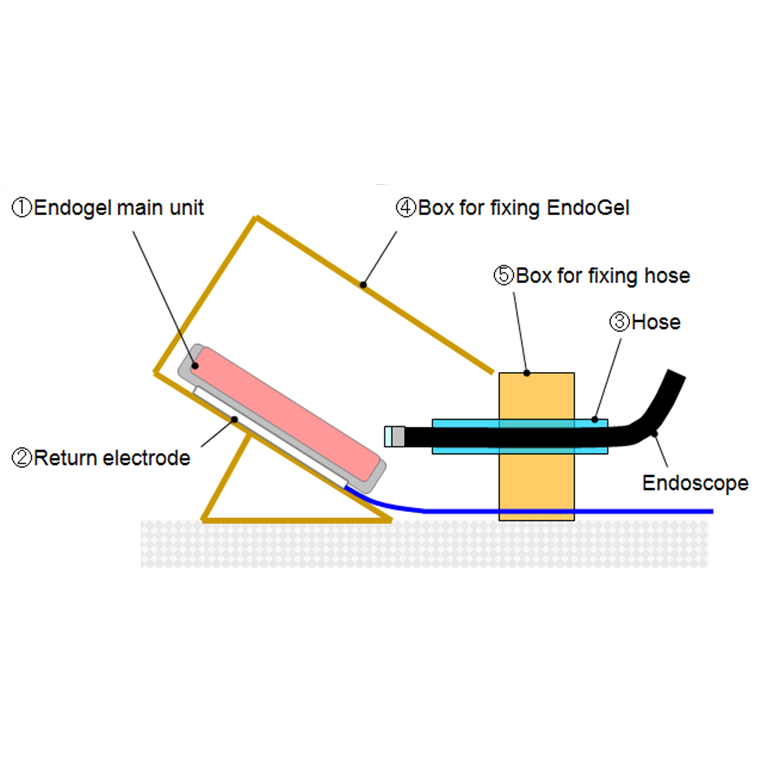
ESD Endogel Model
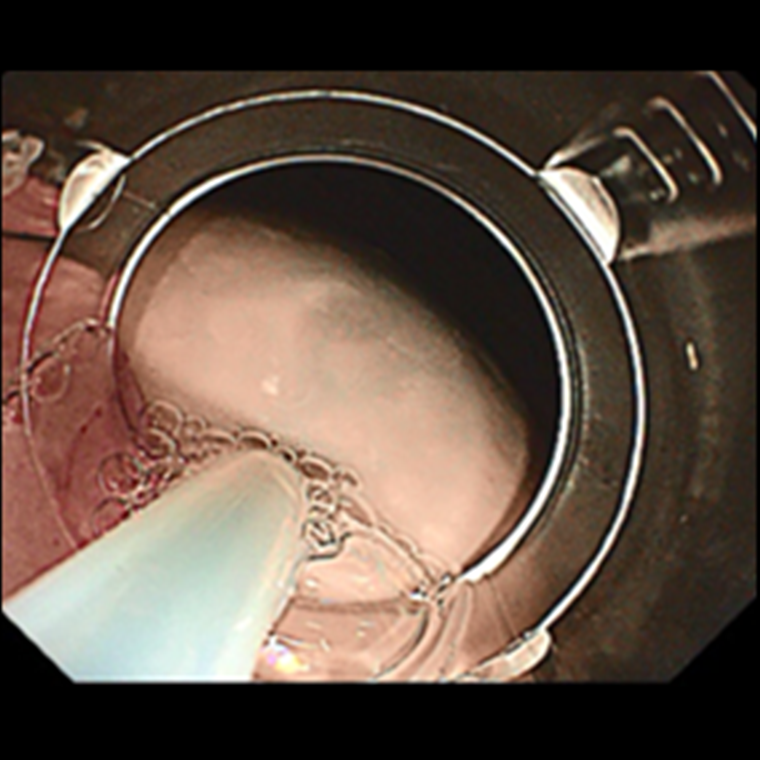
Submucosal Injection
Submucosal injection plays an important role in an ESD procedure. The “ideal” submucosal injection solution should be both long-lasting and produce a hemispheric shape to facilitate snaring. In addition, a sufficiently high submucosal elevation is important for safe submucosal cutting.
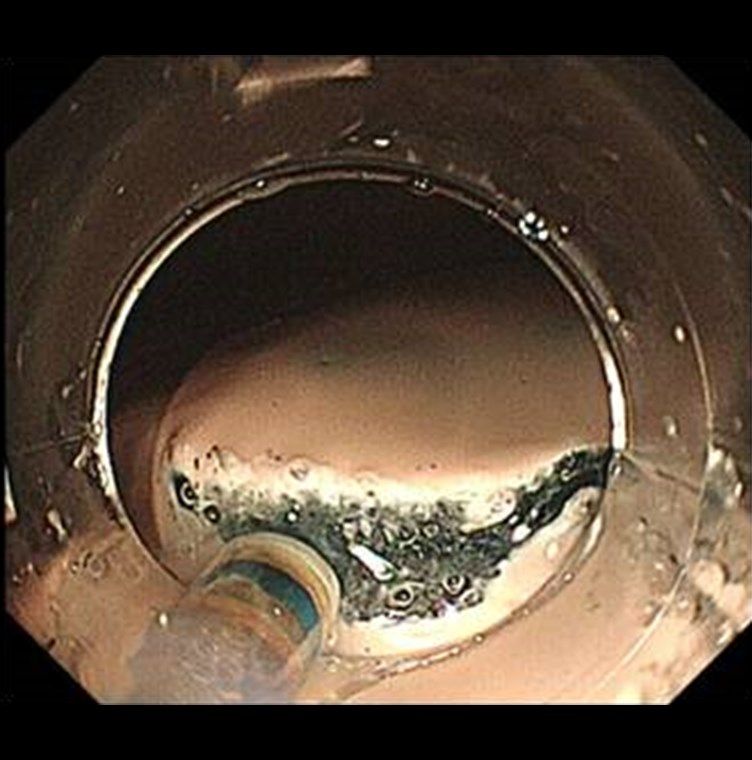
Submucosal Incision
The first step of the submucosal incision is a small cut that penetrates the muscularis mucosa.
Submucosal Dissection
After the initial incision, the exposed submucosal tissue is further dissected by tracing the initial mucosal incision line. This is continued until the submucosal layer is expanded so the scope tip can enter the submucosal space.
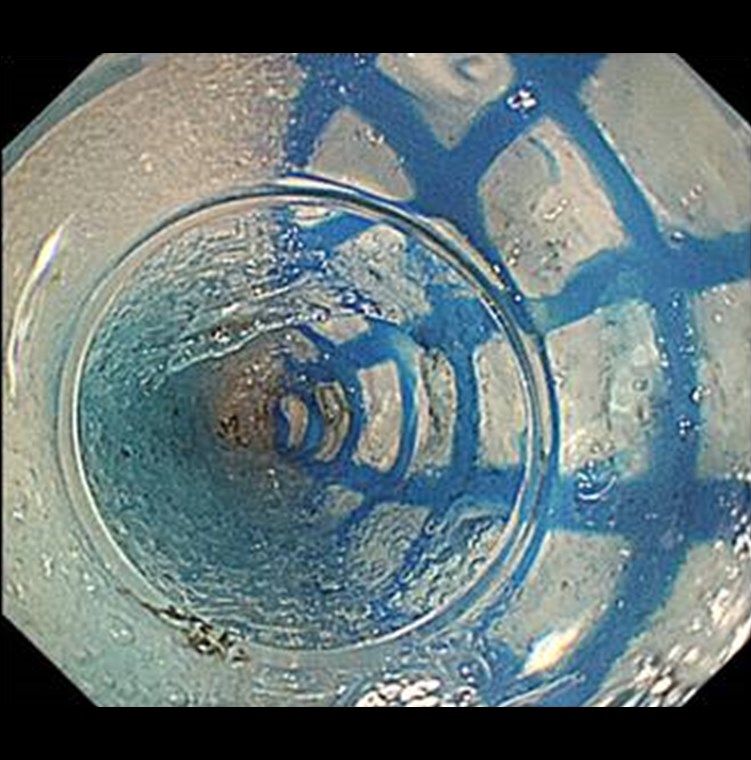


Forming Tunnel (POEM)
Peroral endoscopy myotomy (POEM) is an endoscopic procedure that is performed by creating a short submucosal tunnel in the distal stomach, often along the greater curvature of the stomach. The pylorus is subsequently identified within the submucosal tunnel and divided with an electrocautery device with a goal to minimize any resistance to food passage that may have been related to pylorospasm.
| Brochures | |
|---|---|
| SAendogel - Brochure | Product Manuals |
| ESD Endogel Model - Product Manual |
Brand: Misc Medical |
Code: SAENDOGEL
APN: 9319499129323 |
Supplier Code: ENDOGEL ESD
Brand: Misc Medical |
Code: SAENDOGEL
APN: 9319499129323 |
Supplier Code: ENDOGEL ESD
At a glance
Endogel™ Training Model for ESD/POEM.